How GPS Tracking works
What exactly is GPS tracking, what role do signals from satellites play and how does a GPS receiver work? This article provides an overview of the development and function of the "Global Positioning System".
About GPS tracking
- The Global Positioning System is a satellite navigation system that was originally developed for military purposes. Today, GPS systems are widely used in the civilian sector.
- GPS tracking is used to locate objects. There is a difference between passive and active tracking. Only with the latter is it possible to locate moving objects in real time.
Whether driving, cycling or hiking, in agriculture, mining or the financial system, GPS now affects almost every aspect of our lives. But how does the technology that we take for granted in sat navs or when using Google Maps work, and how was it developed? Here we take a look at the secrets of GPS technology. We focus on its function in the mobility sector.
What is GPS Tracking: A Definition of the Global Positioning System
What is GPS?
GPS (Global Positioning System), officially NAVSTAR GPS, is a worldwide radio navigation system that is currently supported by 24 satellites 6 and their ground stations. The system was originally developed exclusively for military purposes. Today, any civilian user can access GPS signals without any fees or restrictions.
GPS tracking uses satellites that use microwave signals. These waves provide information about the position, speed or direction of objects on earth – one reason why GPS does not work in tunnels, for example.
Understanding GPS Tracking
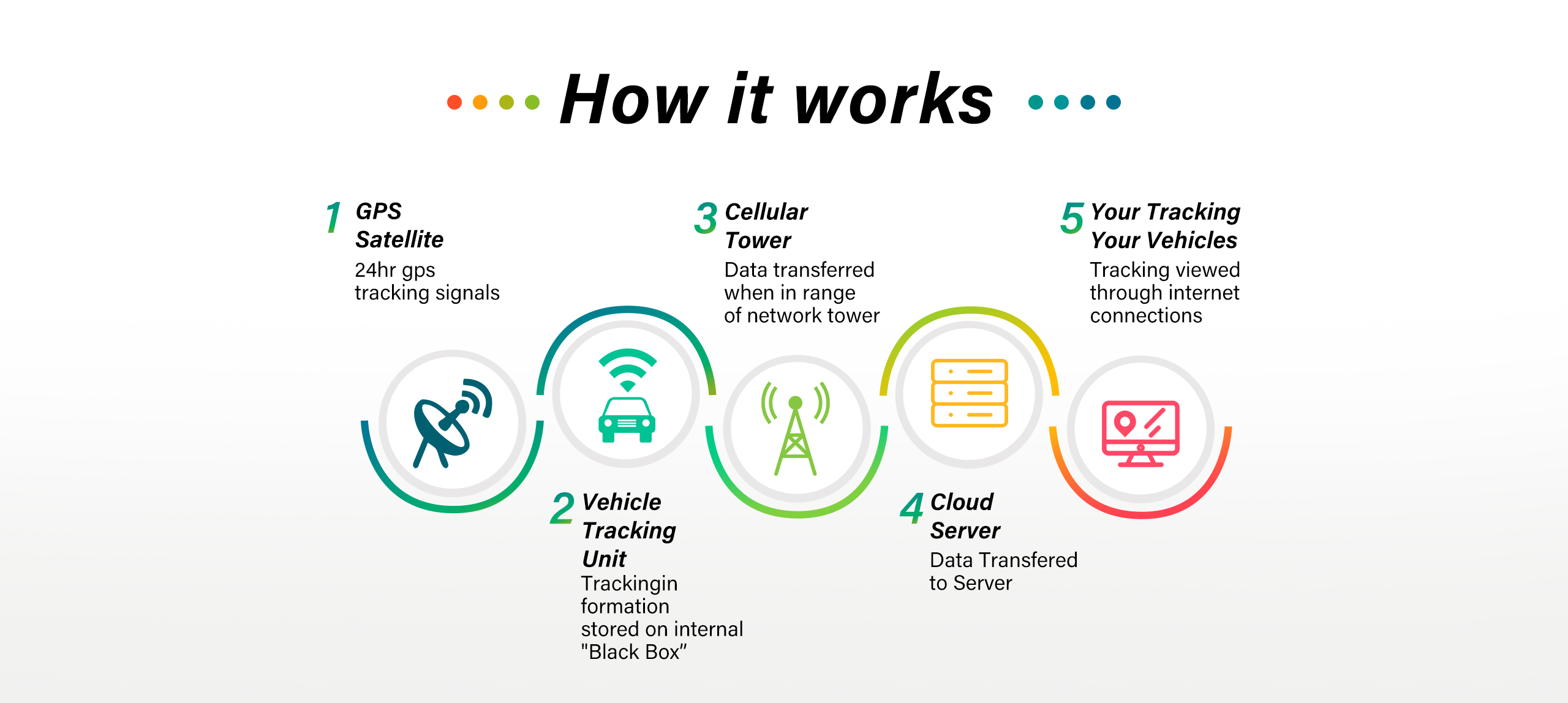
GPS tracking is a method of determining and monitoring the exact location of something. A GPS tracker contains a GPS receiver that collects signals and calculates the coordinates of the object to be located. These are transmitted via an internet connection through cellular, Wi-Fi, or radio frequencies. A tracking system can be attached to a vehicle or cell phone, for example, and can be permanently installed or portable.

From GPS Satellites and Navigation systems – the History of the GPS Tracking System
The US Air Force initially developed GPS with the aim of improving its military operations. It replaced radio navigation systems such as LORAN and DECCA .
The development of GPS began in 1958, when Soviet experts sent the first satellite called Sputnik into space. Scientists at MIT observed that the satellite’s radio frequencies changed depending on its location. This Doppler effect, the changing frequency emission of satellites, gave them the idea that the position of a satellite along its orbit around the earth could be tracked or traced directly from the ground by calculating the radio frequency variations of a signal.
TRANSIT and ESTIMATION
The first navigation satellite system TRANSIT
US Navy scientists developed the first navigation satellite system, called TRANSIT. Now the navy could locate its submarines equipped with nuclear missiles. The TRANSIT technology used five constellation satellites. The system was first successfully put into practice in 1960.
The ESTIMATION technology
Five to six years after the implementation of TRANSIT, the US Navy, with the help of MIT scientists, developed another satellite called ESTIMATION. This satellite made it possible to place precise clocks in space. GPS is still based on ESTIMATION technology today. In the early 1970s, Omega was developed, the world’s first ground-based navigation system, which was the first radio navigation system to be implemented and put into operation. Later, Rockwell International launched the Block I GPS satellite. In 1983, after a Soviet interceptor shot down a civilian airplane that had strayed into restricted Soviet airspace. Afterwards, the US president announced that GPS tracking devices could be used by everyone as soon as they became available.

NAVSTAR and the first GPS Satellite
Eventually, private technology companies such as Aerospace began to help the US military develop another satellite in orbit that would constantly receive and continuously transmit signals from the ground. After ten years of development, the US Air Force launched the first satellite of the 24-satellite tracking system NAVSTAR, or GPS as it is known today.
For a long time, the GPS system was only approved for civilian use with limited accuracy. An interference signal reduced this to around 100 meters. It was not until 2000 that the selective GPS availability was lifted.
In the course of time, the number of active, oscillating satellites and the reserve inventory was also steadily increased and the accuracy of the GPS improved. Scientists, private companies and the US Department of Defense developed a growing number of GPS-based applications.
How does GPS work?
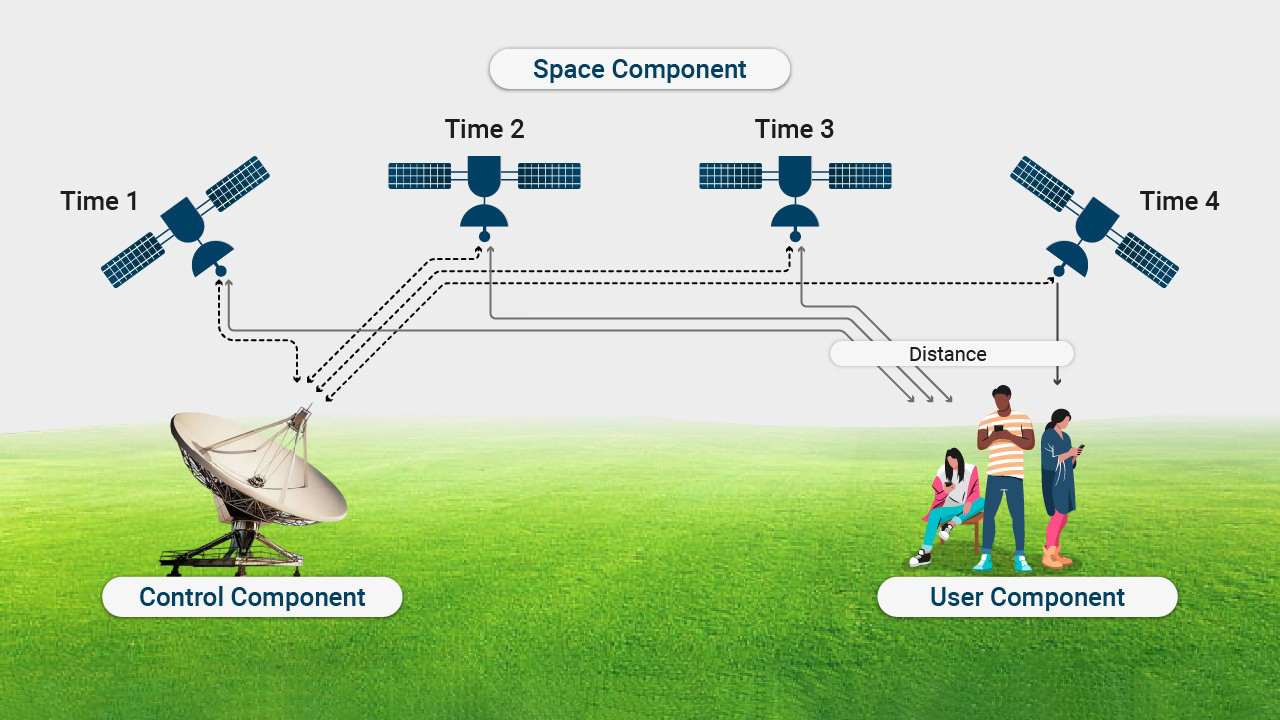
GPS uses the mathematical principle of trilateration. In order for the GPS to perform mathematical calculations, it must know at least two aspects:
1.the current location of the person, object or vehicle, which is targeted by at least three satellites and
2.the distance or current range between the object to be tracked and the tracking point.

One GPS satellite is not sufficient to obtain information about the exact location of a moving object. At least three GPS satellites are required, in many cases even at least four.
GPS receivers usually record the position of an object as it moves from one point to another.
A GPS tracker basically has two functions:
1.storing the recorded data on the device itself (passive tracking) and
2.regularly sending the recorded data to a central system via a modem attached to the GPS device (active positioning).
Different Types of Global Positioning System
Passive Global Positioning System
The passive global positioning system monitors the location of a moving vehicle based on certain driving events. Passive GPS direction finders, for example, record the locations that the vehicle has passed in the previous hours. The information is stored on the internal memory or on an external device such as a memory card and later transferred to a computer for analysis. Sometimes stored data is automatically sent via the Internet and downloaded at a specific point or retrieved while driving.

Active Global Positioning System
With active GPS (live tracking), for example, a GPS-enabled tracking device is installed on a car to collect tracking information to determine its position and transmit it via a satellite or cellular network.
If the cellular network is not available, the GPS transmitter stores the data and transmits it to the server as soon as the cellular network is available again. Real-time tracking applications are ideal for theft protection. They can be used, for example, to pinpoint the exact location of stolen vehicles.
Mini GPS Tracker
“Mini GPS tracker” is a popular term for trackers of the active Global Positioning System. Mini GPS trackers are often used in security applications, for example to monitor people, children or pets or to protect vehicles such as trucks, cars or motorcycles from theft. Modern devices usually communicate with the user via a smartphone app.
GPS Tracker for People and Animals
A mini GPS tracker for people, children or animals should be handy, light and above all inconspicuous, as it has to be worn. Devices that are attached to the collar of (pets) animals should also be waterproof if the pets spend a lot of time outdoors. It better to be waterproof and inconspicuous. One of its most important functions is the “Geo-fence": The owner receives a notification when the people or pet leaves a defined area.
Vehicle Tracker
A mini GPS tracker is also an ideal anti-theft device for tracking stolen vehicles. Equipped with a SIM card and lightweight electronics, it should be no more than around seven to eight centimeters in size. It can even be fitted in the rear lights of trucks. If a mini GPS tracker is integrated into vehicles, the likelihood of the tracker being detected decreases.
But it’s not just the size that matters. One of the most important quality features is the battery life of a tracker. The smaller the device, the smaller the battery, the shorter the battery life. If the GPS tracker is not connected to a power source, the battery will need to be recharged after a few hours or days. The situation is different with mini GPS trackers that are integrated into a car and are powered directly by its battery, such as wired GPS Tracker, OBD II Tracker.
The interaction of GPS Trackers and Tracking Apps
Tracking apps establish a connection between a GPS transmitter and a smartphone. The tracker does not communicate directly with the owner’s cell phone, but sends the data to an intermediary server. This forwards the data to the GPS app on the cell phone. The receiver attached to vehicles such as cars or e-bikes helps the owner of the corresponding cell phone with the tracking app to determine the exact position of their vehicle or to view its route if they are involved in an accident or the vehicle is stolen.
The GPS signal is transmitted to the smartphone via mobile phone standards of different generations such as 2G, 3G, 4G (second, third and fourth generation) etc. GPRS and LTE are the designations for data transmission within these generations. GPRS is the data transmission within the 2G standard and LTE stands for data transmission within the 4G standard.
Summary
With GPS tracking, information about the exact position of a vehicle or person is transmitted via mobile radio, Wi-Fi or radio frequencies. The tracking itself works with a radio navigation system that is currently supported by around 24 satellites and their ground stations. GPS trackers are able to provide previous (passive) and real-time (active) navigation information about a journey. A mini GPS tracker is part of the active global positioning system (real-time GPS tracking). It is particularly suitable for locating people or animals as well as for theft protection of vehicles such as trucks, cars or e-bikes. The size of the GPS receiver determines its battery life.
A key advantage of GPS receivers is that they can be used to better secure assets. They are also important for navigation. Companies can use GPS tracking to optimize their processes. However, GPS receivers are dependent on data from at least three satellites, usually even four. Without sufficient satellite signals, real-time positioning is not possible.
Therefore, the use of GPS services is charged on a monthly basis, whether it is 4G traffic or satellite base stations. In other words, the data transmission of GPS trackers is similar to that of mobile phones. Relying on GPS and global cellular, you have to pay for the SIM card.